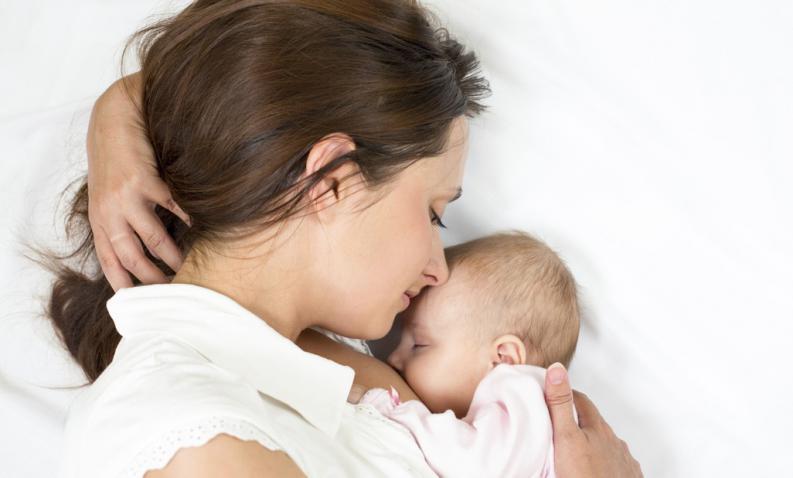
The first days of breastfeeding are fundamental: in order not to go into crisis waiting for the whipped milk, not to give in to the temptation to give (or make him give) additions in fear that one’s milk is not enough, in short, in order not to send the milk upstream breastfeeding even before starting.
Trust, you can do it! 99 percent of mothers are physiologically capable of breastfeeding
Know that practically all women have the potential to breastfeed and that women who for physiological reasons cannot feed their child on the breast are very few, only 1 percent of the total. The remaining 99 percent are physiologically capable of breastfeeding , just starting on the right foot.
Start breastfeeding as soon as possible
The sooner you breastfeed your baby, the better: the ideal would be within two hours of birth or even earlier, if possible, because at that moment the baby’s sucking instinct is very high and because these first “early” feedings are essential because the child receives the colostrum , the serum that is secreted before the arrival of the whipped milk which contains a cocktail of antibodies very valuable for his immature immune system.
To achieve this goal, skin-to-skin contact between mother and baby immediately after delivery is very important.
Long live breastfeeding on request
The first rule to breastfeed exclusively is to satisfy the baby’s requests. The more the baby gets attached, the more the milk production is stimulated , in a game of supply and demand that fully satisfies the needs of the baby and helps to avoid the annoying traffic jams of the first days of breastfeeding.
Breastfeed without watch in hand
Breastfeeding does not want strict rules: no 10 minutes breastfeeding or breastfeeding every 3 hours. The child must be able to attack himself as often as he wants and for as long as he wants : when he is satisfied, he will spontaneously detach or fall asleep. It is true that, little by little, the child learns to eat at a more regular pace, but we must not believe that this will happen in a few days!
We repeat it: attach it on request!
Especially in the first few days, the baby seems insatiable: he has just finished drinking, falls asleep and, after less than half an hour, he still claims milk. Everything is normal: in the first weeks the baby is looking not only for nourishment but also consolation and comfort in the breast . In addition, the maternal food, being very digestible, is quickly assimilated, so it is natural that after a short time the baby asks for more.
Avoid double weighing
Weighing the baby before and after feeding just risks generating anxiety: there are feedings in which he drinks more, others in which he takes only a few sips, some in which milk has a less protein-rich composition, others in which it is fatter and nourishing, therefore it satisfies even with smaller quantities. To check its growth, just weigh it once a week in the first months , and then gradually reduce the frequency of weighing up to one a month. If you have doubts, check how many diapers you get wet: if they are at least 6/8 in 24 hours and if you discharge at least 2 or 4 times, it means that you eat well and are hydrated.
Take into account the night feedings
Especially in the first few weeks, the baby needs to eat at more or less regular intervals and makes no distinction between daytime and nighttime, so it is normal for the night to wake up to suck. Put it into account and gladly accept its awakenings. Maybe for greater comfort in the early days you can keep the baby in a cot next to your bed, so you will be more comfortable managing the feedings.
Finally, remember that during the night hours prolactin , the hormone responsible for milk production, is more active : one more reason not to miss such an important appointment!
The baby sleeps, sleep too!
It is known, the first days will come the visits of relatives and friends who want to know the newborn. Don’t worry about it if the house is not in perfect order: guests will understand! Indeed, if you have a mom or sister available, take advantage of it to help you with the chores of the house, otherwise send back everything that is not really essential. Rather, try to rest when the baby also sleeps, so when he wakes up you will be more relaxed and available towards him and you will face the nighttime awakenings with more serenity. Breastfeeding is an important commitment , don’t get distracted by unnecessary activities!
Breastfeeding problems for the newborn
Difficulty attaching the infant to the breast
The infant must be able to attach itself to the breast in order to grow and stimulate milk production.
Prematurity, maternal anesthesia during childbirth, jaundice, infections, chronic diseases (e.g. heart disease) can cause difficulty sucking or poor coordination between sucking, swallowing and breathing. In other cases the cause of the sucking difficulty can be “mechanical”: a short lingual frenulum or a lip / cleft palate can directly interfere with the ability of an effective suckling of the newborn.
Possible signs of ineffective suckling of the newborn:
- He does not wake up alone to claim milk at least 6-7 times in 24 hours
- Claim milk more than 13-14 times in 24 hours.
- It attaches and detaches repeatedly from the breast.
- It resists sticking to the breast.
- He falls asleep after sucking for only 4-5 minutes.
- It remains attached to the breast for over 30-40 minutes without spontaneously detaching itself.
- Wet less than 6 diapers in 24 hours (after the end of the first week of life).
Even looking at the mother’s breasts one can suspect an ineffective sucking:
- There are fissures, redness or pain in the nipples.
- The breasts are not swollen before breastfeeding or do not soften after feeding.
- There is breast engorgement or mastitis.
Slow or poor growth
Weight gain is one of the signs of good health of the newborn and, although slow growth can occur in perfectly healthy children, this is often a sign of some problem. If the newborn does not gain weight adequately according to certain growth charts, it is necessary to contact the pediatrician to investigate the possible causes of the problem.
Attention signs are:
- The infant does not regain the birth weight within 15 days.
- It does not grow at least 150 grams per week after recovery of birth weight.
- The growth rate of the newborn decreases significantly and suddenly.
Tips for a good breastfeeding
If after the first week of life the newborn still has difficulty attaching properly to the breast, do not be discouraged: almost all babies learn to attach themselves to the breast if we give them the chance.
- Postponing the meal to try to lengthen the time between feedings or offer a pacifier instead of the breast when the newborn is hungry is wrong and can cause poor growth.
- If the infant is “lazy”, grows little and does not wake up at least 6-7 times in 24 hours to eat, it may be necessary to wake him up to breastfeed him more often (even every 2 hours during the day and every 3-4 hours at night ) until he regains weight.
- Skin-to-skin contact seems to help newborns understand how to attach themselves to the breast and helps stimulate and maintain milk production.
- Babies, when they are very covered, feeling warm and safe tend to doze off quickly during meals; it is therefore advisable to dress them in light clothing.
- If the baby falls asleep a few minutes after attaching to the breast, you can try massaging the breast and reactivating sucking by moving the nipple in the baby’s mouth. Massaging the breast with circular movements downwards and towards the nipple also helps to flow milk into the baby’s mouth.
- In general, avoid changing breasts and go to the other after a few minutes of breastfeeding, because in this way the infant does not take the final milk contained in the breast, richer in calories. In some cases, however, the maneuver to change breasts can help a “lazy” infant to wake up and start sucking again.
- If the breasts are too full, use a breast pump after the end of the feed to avoid the milk jam.
- If the infant is able to attach to the breast, but is unable to suck, it may be helpful to simultaneously pull the milk from the other breast with a breast pump.
- In some cases it may be necessary to offer additional calories to the newborn by giving him the previously pulled milk or formula milk. Follow the pediatrician’s advice to determine the amount of supplementation.
- You must be patient and not discouraged if the baby takes time to learn, if you are in difficulty, let yourself be helped and consult a breastfeeding expert or one of the numerous associations that support breastfeeding.
In any case, it is essential to contact the pediatrician if, once checked that breastfeeding takes place correctly, the infant continues to not grow adequately.